USB Standards Explained: Your Ultimate Guide to Type-C, Speeds, and Charging Watts
USB Standards Explained. USB (Universal Serial Bus) is everywhere, powering our phones, charging our laptops, and moving massive amounts of data. But with a chaotic naming scheme, ever-changing ports (A, B, C, Micro), and confusing standards (USB 2.0, 3.2, Gen 2×2!), it’s nearly impossible to know if you’re buying the right cable.
This guide will demystify modern USB standards explained simply, so you always know exactly what cable you need for maximum speed and power.
1. Connector Types: The Shape of the Port
The first layer of confusion is the physical connector. Today, one type dominates the market:
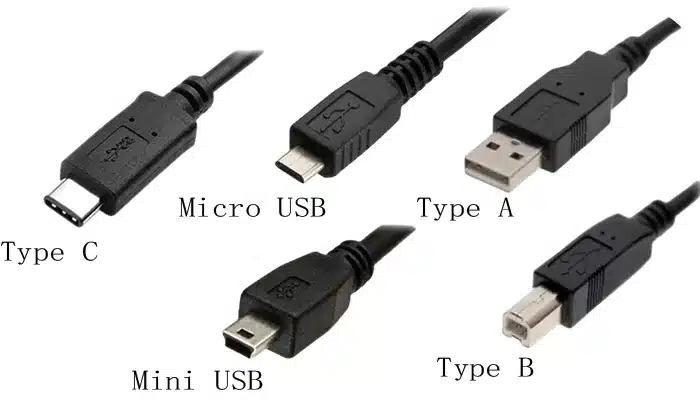

A. USB Type-C (The Modern Standard)
- Appearance: Small, oval, and reversible—it plugs in both ways.
- The Future: Type-C is not just a connector; it’s a foundation. It supports all the fastest current USB standards, can deliver up to 240W of power, and can carry video signals (DisplayPort Alt Mode).
B. Older/Legacy Connectors
- USB Type-A: The familiar rectangular connector (e.g., on your PC tower). Still used widely on host devices.
- USB Type-B: Square-shaped (e.g., used for printers).
- USB Micro-B: Small, trapezoidal shape (e.g., used on older smartphones and accessories).
2. Speed Standards: How Fast is Your Data?
This is where most of the confusion lies. The current naming conventions are based on the maximum theoretical data rate (measured in Gigabits per second, or Gbps).
| USB Name (Official Standard) | Common Marketing Name | Max Speed (Gbps) | Key Features |
| USB 3.2 Gen 1 | USB 5Gbps / USB 3.0 / USB 3.1 Gen 1 | 5 Gbps | First to introduce SuperSpeed (SS) data transfer. |
| USB 3.2 Gen 2 | USB 10Gbps / USB 3.1 Gen 2 | 10 Gbps | Twice the speed of Gen 1. The minimum for modern fast storage. |
| USB 3.2 Gen 2×2 | USB 20Gbps | 20 Gbps | Uses two 10Gbps lanes simultaneously (hence 2×2). Requires compatible hardware and specific cables. |
| USB4 | USB 40Gbps | 20 or 40 Gbps | Based on Thunderbolt 3 protocol. Enables tunneling of DisplayPort and PCIe. |
| USB 2.0 | Hi-Speed USB | 480 Mbps | Legacy standard, sufficient only for keyboards, mice, and basic charging. |
Key Insight: When shopping, ignore the “3.x” and look for the speed number (Gbps). A cable labeled “10Gbps” is twice as fast as one labeled “5Gbps,” regardless of the Gen/Version number used.
3. The Power Equation: Charging and Power Delivery (PD)
Speed isn’t just about data; it’s about charging capacity, which is governed by USB Power Delivery (USB PD).
A. Standard Charging (Legacy)
Older USB 2.0 ports provided just 2.5W (5V/0.5A). Even basic phone chargers today start at 7.5W to 15W.
B. USB PD (Modern Fast Charging)
USB PD is a specification that allows devices to communicate and negotiate charging power up to very high levels.
- Standard USB PD (Pre-2021): Supported up to 100W (20V/5A), sufficient for most laptops.
- Extended Power Range (EPR): The newest standard allows power delivery up to 240W (48V/5A). This is necessary for high-performance gaming laptops and powerful accessories.
Crucial Cable Check: To use power above 60W (e.g., 100W or 240W), your cable must be specifically designated as an e-marker cable. This embedded chip communicates the cable’s power limit to the connected devices, ensuring safety.
4. The Built By Pete Cable-Buying Checklist
When purchasing a cable, focus on what the marketing claims about its capabilities, not just its connector shape.
- Check the Connector: Ensure it’s USB Type-C at the device end.
- Check the Speed: Look for 10Gbps as a minimum for data transfer, or 40Gbps for cutting-edge performance (often includes Thunderbolt).
- Check the Power: Look for the Watt rating. If you need more than 60W for your laptop, ensure the cable is rated for 100W or higher and explicitly states it contains an e-marker chip.
Understanding these few key numbers is the only way to cut through the marketing noise and guarantee you’re not bottlenecking your fast charger or external SSD.
Watch the video in full Test USB Cables with a USB Power Meter Must Have USB Cable Power Tester
Subscribe Now!
If you found this USB Standards Explained guide helpful and are ready to stop guessing and start troubleshooting your own tech plus smart DIY, head over to the Built By Pete YouTube channel! We’ve got the full video walk through showing exactly how to use this gadget, plus dozens of other DIY projects and smart home tutorials. Click here to subscribe and hit the notification bell so you never miss out on the tips, tricks, and step-by-step guides that will simplify your tech life.




